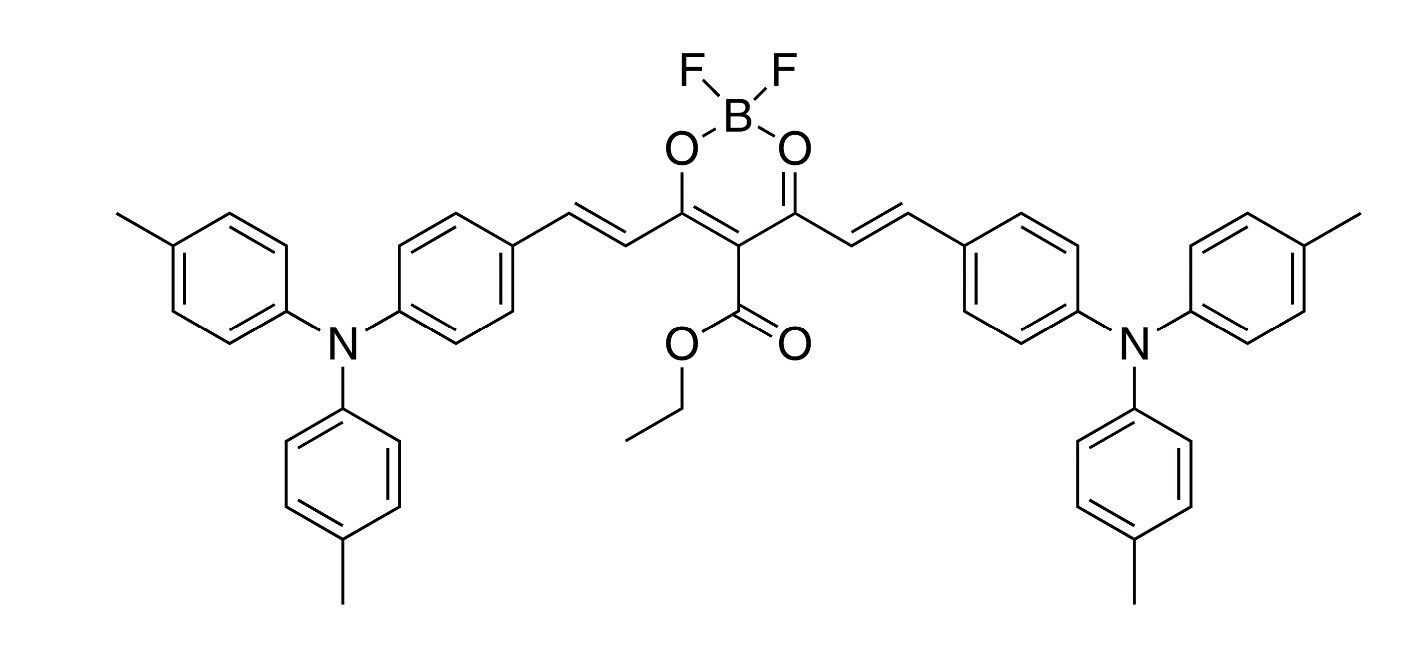
TPAM-BF2
Product Description
TPAM-BF2, identified as 4,6-Bis((E)-4-(di-p-tolylamino)styryl)-5-(ethoxycarbonyl)-2,2-difluoro-2H-1,3,2-dioxaborinin-1-ium-2-uide, is a complex organic compound showcasing a dioxaborinine ring system with styryl groups and ethoxycarbonyl substitution. This molecular structure confers upon TPAM-BF2 unique electronic and optical properties, making it a subject of interest in the field of organic electronics. Its ability to facilitate efficient charge transport mechanisms is particularly noteworthy, positioning it as a potential candidate for enhancing the performance of electronic devices such as OLEDs (Organic Light Emitting Diodes) and solar cells. Furthermore, TPAM-BF2 exhibits good thermal stability and solubility characteristics, expanding its utility across various technological applications.
Application
TPAM-BF2 finds its primary application in the development of advanced organic electronic components, specifically in OLED technology and photovoltaic devices. Its molecular design supports efficient charge transport, crucial for improving device efficiency and longevity. Additionally, TPAM-BF2's thermal stability makes it suitable for high-temperature operational environments, further broadening its integration possibilities into electronic materials and systems.
Articles:
- Efficient Solution-Processed Hyperfluorescent OLEDs with Spectrally Narrow Emission at 840 nm
Publication Date: 10 November 2020
Afshin Shahalizad, Alexandre Malinge, Lei Hu, Grégory Laflamme, Louis Haeberlé, David M. Myers, Jian Mao, William G. Skene, Stéphane Kéna-Cohen
https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202007119
- Harvesting triplet excitons for near-infrared electroluminescence via thermally activated delayed fluorescence channel
Publication Date: February 02, 2021
You-Jun Yu, Xue-Qi Wang, Jing-Feng Liu, Zuo-Quan Jiang, Liang-Sheng Liao